Data Transformation
What is Data Transformations
Data Transformations are useful tricks for making certain types of data easier to model.
A transformation is a rescaling of the data using a function. When data are very stongly skewed, sometimes we transform them so they are easier to model.
(Natural) log transformation
The most commonly used transformation is the natural log transformation. Natural log transformation is often applied when:
- Much of the data cluster near zero (relative to larger values in the data set).
- and, all observations are positive.
Here is the distributions of income per person, it is heavily right skewed, but after applying natural log transformation the data become much more symmetric. Sometimes this type of data are much easier to model because they are much less skewed and outliers are usually less extreme.
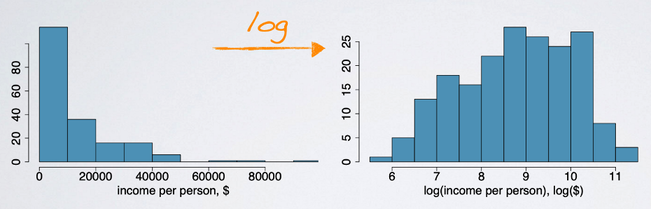
Transformations can also be applied to one or both variables in scatterplot to make the relationship between variables more linear, and hence easier to model with simple methods.
For example:Here is a scatterplot of income per person versus life expectation. The relationship is positive and curved, after applying a log transformation, the relationship stays positive but becomes more linear, which makes it easier to model than the untransformed data.
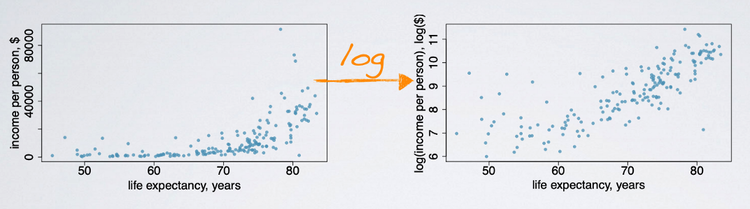
Other transformations
In addition to the log, we can also try a square root transformation, where we plot the square root of the weight versus miles per gallon. Or the inverse transformation, where we divide 1 by the weight of the car.
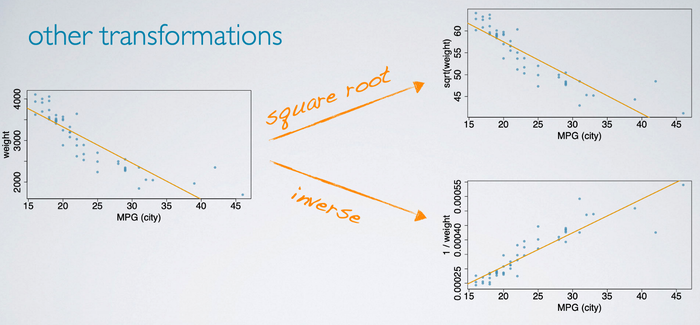
It is difficult to tell just looking at these plots which transformation works better, or if either of the transformations actually yield something better than the original data.
Goals of Transformations
It is important to understand why we need to apply a transformation in the first place. So, here is the common goals in transforming data.
- To see the data structure differently
- To reduce skew assist in modeling
- To straighten a nonlinear relationship in a scatterplot so that we can model the relationship with simpler methods.
Latest Post
- Dependency injection
- Directives and Pipes
- Data binding
- HTTP Get vs. Post
- Node.js is everywhere
- MongoDB root user
- Combine JavaScript and CSS
- Inline Small JavaScript and CSS
- Minify JavaScript and CSS
- Defer Parsing of JavaScript
- Prefer Async Script Loading
- Components, Bootstrap and DOM
- What is HEAD in git?
- Show the changes in Git.
- What is AngularJS 2?
- Confidence Interval for a Population Mean
- Accuracy vs. Precision
- Sampling Distribution
- Working with the Normal Distribution
- Standardized score - Z score
- Percentile
- Evaluating the Normal Distribution
- What is Nodejs? Advantages and disadvantage?
- How do I debug Nodejs applications?
- Sync directory search using fs.readdirSync