Introduction to Linux
What is Linux
- An Operating System - An operating system is simply a collection of software that manages hardware resources and provides an environment where applications can run. The operating system allows applications to store information, send documents, interact with users etc.
- A Kernel - when the term Linux is used, it refers to Linux Kernel as well. Linux Kernel is a layer that sits between the hardware and applications. In another way, it is the intermediary between software and hardware. However, to have a useful operating system you need other components in addition to the kernel. These components can include system libraries, graphical user interfaces, email utilities, web browsers, and other programs.
- Created by Linus Torvalid - He created Linux when he was a student at the University of Helsinki, studying computer science. Driven by the desire to run a UNIX-like Operating System on his personal computer, he set out to create Linux.
- First version released in 1994 - Kernel V1.0
- FOSS (Free/Open Source Software) - This means that anyone can use, copy, study and change the software in any way they choose, so long as the source code is openly shared with others. In every case the source code is free, but in some cases the distribution (binaries, the compiled code) is not free. E.g. You need to pay a license to run Red Hat Enterprise Linux. However, Red Hat release the source code for anyone to download.
- UNIX-like - Linux is not a UNIX derivative. Linux was written from scratch, however many commands that are found in Linux are also found on UNIX.
Linux Distributions
- Linux Kernel Plus Additional Software - It is the Linux Kernel and a collection of software that together create an operating system.
- Each distribution can have a different focus - Your choice of distribution will depend on wht you are trying to accomplish.
- Many distributions available to chose - Commercial and non-commerical. Commercial Linux distributions are backed by corporations, and you can buy support from them. You have Linux distributions that are designed for server use, others that are designed for desktop use. Some are focused on research and science, others are focused on multimedia production.
There are literally hundreds of Linux distributions. DistroWatch.com is a great website to learn about all the available Linux distributions.
Here are some popular Linux distributions:
- Red Hat Enterprise Linux
- Fedora
- Ubuntu
- CentOS
- SuSE Linux Enterprise Server
- OpenSuSE
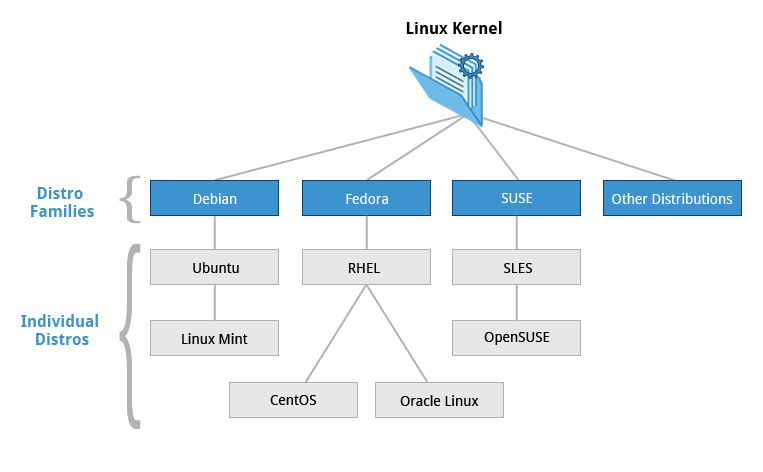
Linux Distribution Families
There are three major distribution families:
- Debian Family Systems (such as Ubuntu)
- SUSE Family Systems (such as openSUSE)
- Fedora Family Systems (such as CentOS)
Reasons to use Linux
- Runs on many hardware platforms - From dedicated networking devices to phones to personal computer and even super computers. Proprietary UNIX operating systems typically on run on their hardware from their company. For example: HP-UX only runs on HP servers, AIX only runs on IBM servers. Linux can run on HP, IBM and other servers. Linux was developed on PC hardware using Intel processors.
- Small Footprint - The small footprint of linux, allows it to run on older hardware or on embeded systems.
- Stable, Reliable and Secure - This make it a great choice for servers that need to continuously run without down time.
- Great for servers - Linux has traditionally been used for server applications. Lin can be used to host websites, act as file servers, and run database software.
- FOSS - Linux is free, not only the source code but also you can run Linux on your hardware without having to pay a licensing fee in many cases. Linux is also free in the sense that you can use it for any purpose, , and you can modify it to fit your requirements.
Latest Post
- Dependency injection
- Directives and Pipes
- Data binding
- HTTP Get vs. Post
- Node.js is everywhere
- MongoDB root user
- Combine JavaScript and CSS
- Inline Small JavaScript and CSS
- Minify JavaScript and CSS
- Defer Parsing of JavaScript
- Prefer Async Script Loading
- Components, Bootstrap and DOM
- What is HEAD in git?
- Show the changes in Git.
- What is AngularJS 2?
- Confidence Interval for a Population Mean
- Accuracy vs. Precision
- Sampling Distribution
- Working with the Normal Distribution
- Standardized score - Z score
- Percentile
- Evaluating the Normal Distribution
- What is Nodejs? Advantages and disadvantage?
- How do I debug Nodejs applications?
- Sync directory search using fs.readdirSync