What is web application
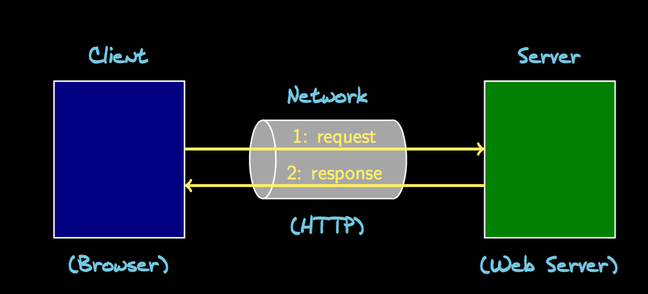
Client-Server Model
The client-server architecture is the most basic model for describing the relationship between the cooperating programs in a web application.
The two parts of a client-server architecture are:
- Server component - "listens" for request, and provides services and/or resources accordingly.
- Client component - establishes a connection to the server, and requests services and/or resources from it.
There is a request/response protocol associated with any client-server architecture:
Web Applications
A web application is accessed by users over a network, uses a browser as the client, and consists of a collection of client- and server-side scripts, HTML pages, and other resources that may be spread across multiple servers. The application itself is accessed by users via a specific path within a web server e.g. www.amazon.com
Other examples including: Webmail, online retail stores, online banks, online auctions, wikis, blogs, document storage, etc.
There is a bit more to it:
Network -
- The internet, a global system of interconnected computer networks.
- Uses the standard Internet protocol suite (TCP/IP)
Web (World Wide Web) -
- A system of interlinked documents (web pages) accessed via the Internet using HTTP
- Web pages contain hypermedia: text, graphics, images, video and other multimedia, along with hyperlinks to other web pages.
- Hyperlinks give the Web its structure
- The structure of the Web is what makes it useful and gives it value.
Advantages -
- Ubiquity and convenience of using a web browser as a client.
- Inherent cross-platform compatibility
- Ability to update and maintain web applications without distributing and installing software on potentially thousands of client computers.
- Reduction in IT costs.
Disadvantages -
- User experience not as good as standalone (workstation/PC) applications - increasingly not the case.
- Privacy and security issues associated with your data
- From a developer's perspective, difficult to develop and debug - there are a lot of moving parts.
References & Resources
- N/A
Latest Post
- Dependency injection
- Directives and Pipes
- Data binding
- HTTP Get vs. Post
- Node.js is everywhere
- MongoDB root user
- Combine JavaScript and CSS
- Inline Small JavaScript and CSS
- Minify JavaScript and CSS
- Defer Parsing of JavaScript
- Prefer Async Script Loading
- Components, Bootstrap and DOM
- What is HEAD in git?
- Show the changes in Git.
- What is AngularJS 2?
- Confidence Interval for a Population Mean
- Accuracy vs. Precision
- Sampling Distribution
- Working with the Normal Distribution
- Standardized score - Z score
- Percentile
- Evaluating the Normal Distribution
- What is Nodejs? Advantages and disadvantage?
- How do I debug Nodejs applications?
- Sync directory search using fs.readdirSync